Mulug Gr
Type Locality and Naming
Lithology and Thickness
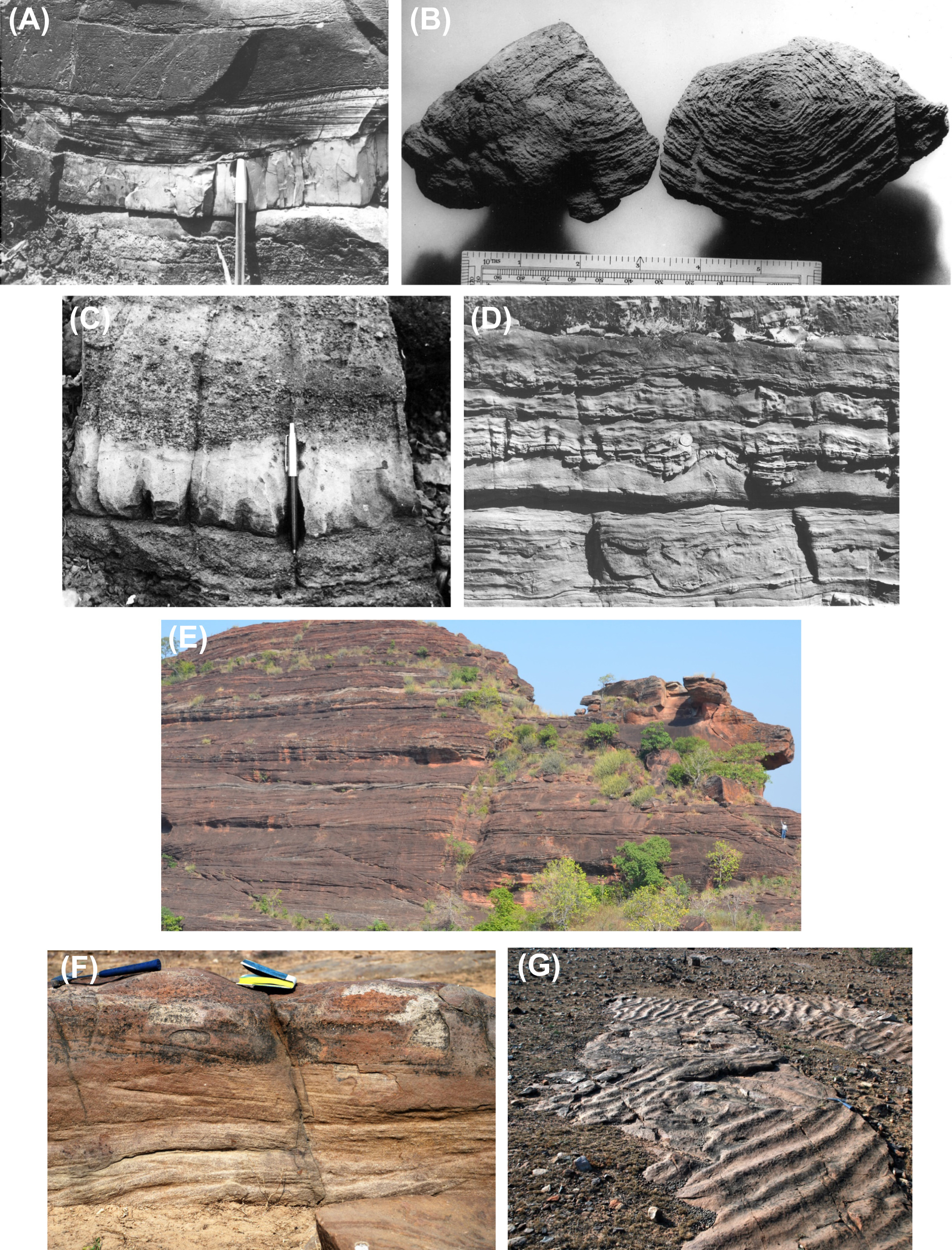
Conglomerate, sandstone and minor chert. Upward succession of Jakaram Conglomerate Fm, Ramgundam Sandstone Fm, Enchencheruvu Chert Fm, and Rajaram Fm. Up to 700 m. (Fig. – images C and D)
[Figure: Pranhita-Godavari valley basin Field photographs illustrating lithology and sedimentary structures. (A) Bollapalli Fm - Sandstones. (B) Pandikunta Limestone Fm - Stromatolites. (C) Jakaram Conglomerate Fm (Damala Gutta Conglomerate Fm) in lower part of Mulug Gr lower part of Mulug Gr - Intercalated conglomerate and sandstone. (D) Rajaram Fm - Limestones. (E) Sullavai Gr Venkatpur Sandstone Fm - Large aeolian cross-strata. (F) Albaka Gr - Cross-stratified sandstone. (G) Somandevara Quartzite Fm - Rippled unit. (H) Bodela Vagu Fm - Laminated lime mudstone. (from Saha et al., 2016)]
Relationships and Distribution
Lower contact
Unconformity, overlies Karlai Shale Fm (Pandikunta Shale Fm) at top of Mallamapalli Gr
Upper contact
Unconformity, overlain by Nalla Gutta Sandstone Fm of Pengnaga Gr
GeoJSON
Fossils
Age
Depositional setting
Basal alluvial fan, upward deepening through tidal flat, chert-dominated outer shelf, then shallowing to back-lagoon and tidal flat.
Additional Information